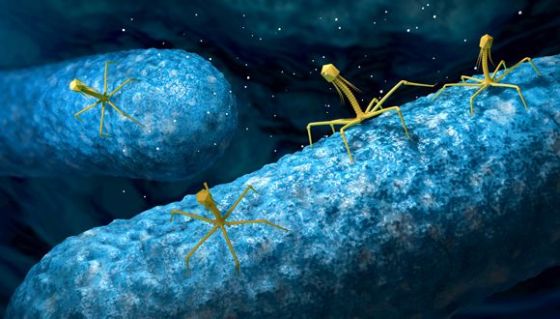
A new TAU study revealed a mechanism through which “good” viruses can attack the systems of “bad” bacteria, destroy them and block their reproduction.
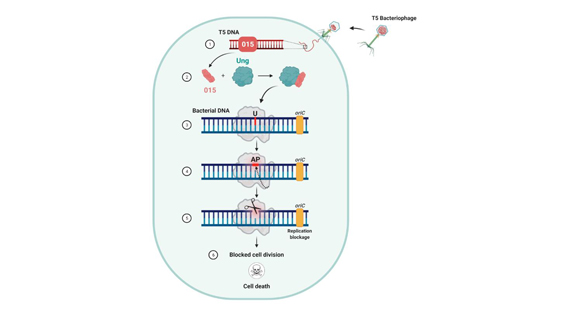 The process by which the bacteriophage destroys the bacteria’s genetic material
Prof. Qimron explains that, “The ability to distinguish between oneself and others is of enormous importance in nature and in various biological applications. All antibiotic mechanisms identify and neutralize bacteria only, with minimal effect on human cells.”
The researchers discovered the process by searching for types of bacterial variants not impacted by this bacteriophage mechanism – those that have developed “immunity” to it. This inquiry led them to the specific bacterial mechanisms affected by the bacteriophage takeover. “Shedding more light on the ways in which bacteriophages attack bacteria, our findings may serve as a tool in the endless battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria,” concludes Prof. Qimron.
Featured image: Illustrative: Bacteriophage or phage virus attacking and infecting a bacterium
The process by which the bacteriophage destroys the bacteria’s genetic material
Prof. Qimron explains that, “The ability to distinguish between oneself and others is of enormous importance in nature and in various biological applications. All antibiotic mechanisms identify and neutralize bacteria only, with minimal effect on human cells.”
The researchers discovered the process by searching for types of bacterial variants not impacted by this bacteriophage mechanism – those that have developed “immunity” to it. This inquiry led them to the specific bacterial mechanisms affected by the bacteriophage takeover. “Shedding more light on the ways in which bacteriophages attack bacteria, our findings may serve as a tool in the endless battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria,” concludes Prof. Qimron.
Featured image: Illustrative: Bacteriophage or phage virus attacking and infecting a bacterium
“Good” Viruses Kill “Bad” Bacteria
The researchers demonstrated that the “good” virus (bacteriophage) is able to block the replication mechanism of the bacteria’s DNA without damaging its own, noting that the ability to distinguish between oneself and others is crucial in nature. The discovery reveals one more fascinating aspect of the mutual relations between bacteria and bacteriophages and may lead to a better understanding of bacterial mechanisms for evading bacteriophages, as well as ways for using bacteriophages to combat bacteria. The study, published recently in PNAS – Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, was led by Prof. Udi Qimron, Dr. Dor Salomon, Dr. Tridib Mahata and Shahar Molshanski-Mor of the Sackler Faculty of Medicine. Other participants included Prof. Tal Pupko, Head of The Shmunis School of Biomedicine and Cancer Research and also of TAU’s new AI and Data Science Center; Dr. Oren Avram of The George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences; and Dr. Ido Yosef, Dr. Moran Goren, Dr. Miriam Kohen-Manor and Dr. Biswanath Jana of the Sackler Faculty of Medicine.A Great Scientific Challenge
Prof. Qimron explains that the antibiotic resistance of bacteria is one of the greatest challenges faced by scientists today. One potential solution may lie in further investigation of the targeted eradication of bacteria by “good” bacteriophages; namely, understanding bacteriophage mechanisms for taking over bacteria as a basis for the development of new tools to combat bacterial pathogens. With this solution in mind, the current study unveiled the mechanism by which the bacteriophage takes control of the bacteria. The researchers found that a bacteriophage protein uses a DNA-repair protein in the bacteria to “cunningly” cut the bacteria’s DNA as it is being repaired. Since the bacteriophage’s own DNA has no need for this specific repair protein, it is protected from this nicking procedure. In this way the “good” bacteriophage does three important things: it distinguishes between its own DNA and that of the bacteria, destroys the bacteria’s genetic material, and blocks the bacteria’s propagation and cell division. The process by which the bacteriophage destroys the bacteria’s genetic material
Prof. Qimron explains that, “The ability to distinguish between oneself and others is of enormous importance in nature and in various biological applications. All antibiotic mechanisms identify and neutralize bacteria only, with minimal effect on human cells.”
The researchers discovered the process by searching for types of bacterial variants not impacted by this bacteriophage mechanism – those that have developed “immunity” to it. This inquiry led them to the specific bacterial mechanisms affected by the bacteriophage takeover. “Shedding more light on the ways in which bacteriophages attack bacteria, our findings may serve as a tool in the endless battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria,” concludes Prof. Qimron.
Featured image: Illustrative: Bacteriophage or phage virus attacking and infecting a bacterium
The process by which the bacteriophage destroys the bacteria’s genetic material
Prof. Qimron explains that, “The ability to distinguish between oneself and others is of enormous importance in nature and in various biological applications. All antibiotic mechanisms identify and neutralize bacteria only, with minimal effect on human cells.”
The researchers discovered the process by searching for types of bacterial variants not impacted by this bacteriophage mechanism – those that have developed “immunity” to it. This inquiry led them to the specific bacterial mechanisms affected by the bacteriophage takeover. “Shedding more light on the ways in which bacteriophages attack bacteria, our findings may serve as a tool in the endless battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria,” concludes Prof. Qimron.
Featured image: Illustrative: Bacteriophage or phage virus attacking and infecting a bacterium