Hyperbaric Treatment More Effective than Medicines for Fibromyalgia Caused by Head Injury
Researchers say “results were dramatic” for patients who underwent hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Researchers from Tel Aviv University compared treatment with a dedicated protocol of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) to the pharmacology (drugs) treatment available today for patients suffering from fibromyalgia, a chronic pain syndrome, caused by traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their findings showed that dedicated hyperbaric oxygen therapy is much more effective in reducing pain than the drug treatment and ended up healing two out of five of the participants in the study.
Chronic Pain Syndrome
The study was conducted by researchers from Tel Aviv University’s Sackler Faculty of Medicine, led by Prof. Shai Efrati, MD, from the Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research at the Shamir Medical Center, and Prof. Jacob Ablin, MD, from the Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center. The results of the study were published in the journal PLOS One.
“At the end of the treatment, two out of five patients in the hyperbaric treatment group showed such a significant improvement that they no longer met the criteria for fibromyalgia. In the drug treatment group, this did not happen to any patient.” Prof. Shai Efrati
“Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome, from which between 2% – 8% of the population suffers,” explains Prof. Shai Efrati. “Until 15-20 years ago, there were doctors who believed that it was a psychosomatic illness and recommended that patients with chronic pain seek mental health care. Today we know that it is a biological illness, which damages the brain’s processing of the signals received from the body. When this processing is malfunctioning, you feel pain without any real damage in related locations.”
“Fibromyalgia can be induced by variable triggers – from certain infections, as we have recently seen in post-COVID patients, through post-traumatic stress syndrome to head injuries. We wanted to test whether the new protocols of hyperbaric medicine can provide better results than pharmacological medicine, for patients in whom the fibromyalgia was induced by traumatic brain injury.”

Prof. Shai Efrati
Dramatic Results
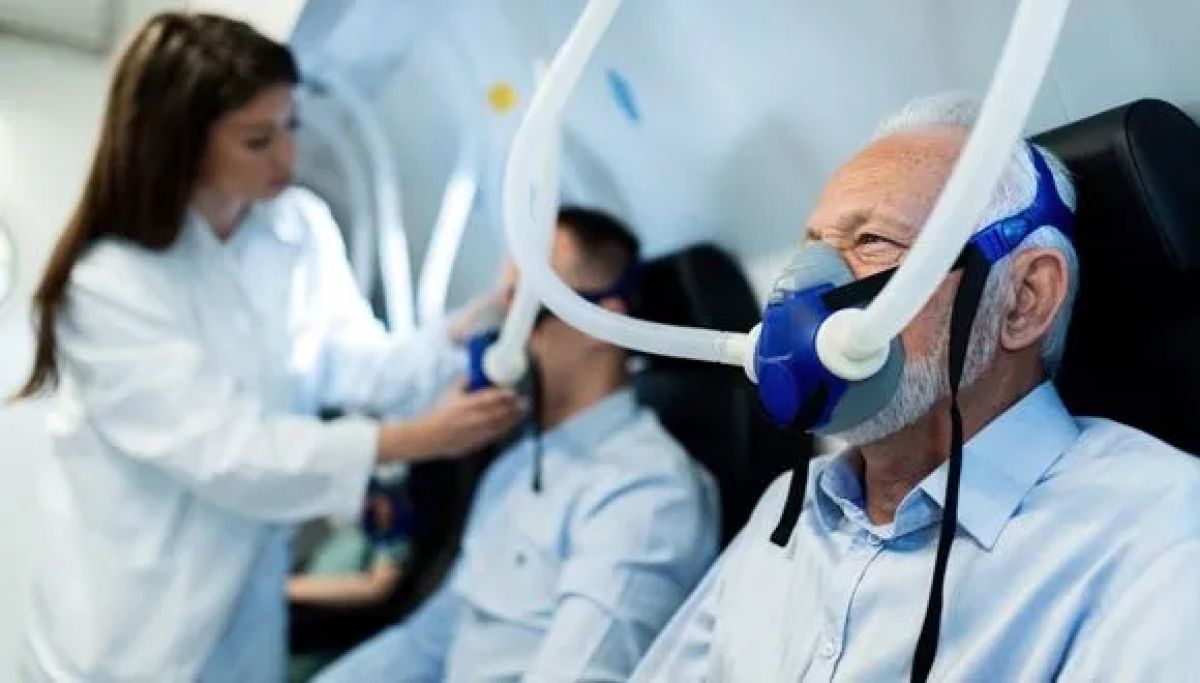
Hyperbaric medicine is a form of treatment in which the patients stay in special chambers where the pressure is higher than the atmospheric pressure at sea level, and where the patients breathe 100% oxygen. Hyperbaric medicine is considered safe, used in many places including Israel, and is already used to treat a long list of medical conditions.
In recent years, scientific evidence has been accumulating that certain, newly developed, dedicated hyperbaric treatment protocols can lead to the growth of new blood vessels and neurons in the brain.
“Overall, existing treatments are not good enough. [Fibromyalgia] is a chronic disease that significantly affects the quality of life, including young people, and hyperbaric medicine meets an acute need of these patients.” Prof. Jacob Ablin
In their current study, the researchers from Tel Aviv University recruited 64 Israelis aged 18 and older who suffered from fibromyalgia as a result of a head injury, and randomly divided them into two groups: one group was exposed to 100% pure oxygen at a pressure of two atmospheres for 90 minutes (with fluctuations in oxygen during the treatment every 20 minutes), five days a week, for three months. The second group received the conventional pharmacological treatment (i.e., the drugs pregabalin, which is known under the trade name “Lyrica”, and duloxetine, which is better known as “Cymbalta”).
“The results were dramatic,” says Prof. Efrati. “At the end of the treatment, two out of five patients in the hyperbaric treatment group showed such a significant improvement that they no longer met the criteria for fibromyalgia. In the drug treatment group, this did not happen to any patient. Furthermore, the average improvement in the pain threshold tests was 12 times better in the hyperbaric group compared to the medication group. And in terms of quality-of-life indicators, as reported by the patients, we saw significant improvements in all the indicators among the patients who received hyperbaric treatment.”
Meets Acute Need
“Today’s accepted treatment for fibromyalgia includes pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic components,” says Prof. Ablin. “with respect to the pharmacologic approach, these drugs are not very effective and therefore the emphasis is on the non-pharmacological side, that is, on external correction of pain processing within the nervous system. Currently used recommendations includes aerobic activity, hydrotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy and movement-based therapies such as Tai Chi. In addition, quite a few patients request treatment with medical cannabis, and for some it helps.”
“In the group that received hyperbaric treatment, you could see the repair of the brain tissue, while in the control group there was only an attempt to relieve the pain – without treating the damaged tissue – and of course the medication group experienced the side effects associated with drug treatment.” Prof. Shai Efrati
“Overall, existing treatments are not good enough. [Fibromyalgia] is a chronic disease that significantly affects the quality of life, including young people, and hyperbaric medicine meets an acute need of these patients. Of course, these are preliminary studies, and we must follow and see what effect the medical protocol has on the patients after one, two and three years – and if it is necessary to maintain the positive results with further exposure to hyperbaric sessions.”
Looking to Cure
According to Prof. Efrati, the importance of the research is in healing the damaged brain tissue – and not in treating its superficial symptoms: “In the group that received hyperbaric treatment, you could see the repair of the brain tissue, while in the control group there was only an attempt to relieve the pain – without treating the damaged tissue – and of course the medication group experienced the side effects associated with drug treatment. This is a difference in approach: to cure instead of just treating the symptoms.”
“We assessed the improvement of the participants in the hyperbaric group more than a week after the last hyperbaric session. More follow-up studies are needed to see the duration of the beneficial effect of the treatment and if and for whom additional treatment will be needed. Our goal as doctors is not only to treat the symptoms but, to the extent possible, also to treat the source of the problem, thus improving the quality of life of fibromyalgia patients.”
“It is important to emphasize that the dedicated hyperbaric oxygen treatment protocol found to be effective is only available in medical centers that have licensed hyperbaric chambers. Be careful of so-called ‘private chambers’, since these cannot provide the therapeutic protocol found to be effective, and they are not regulated or approved for medical use,” cautions Prof. Efrati.